Compute and simulate a repeat ground track orbit
The repeat ground track solver is a numerical routine and notice that it is not exact. The simulation includes the J2 perturbation. See also: RepeatGroundTrack, RHSGeoJ2, GroundTrack
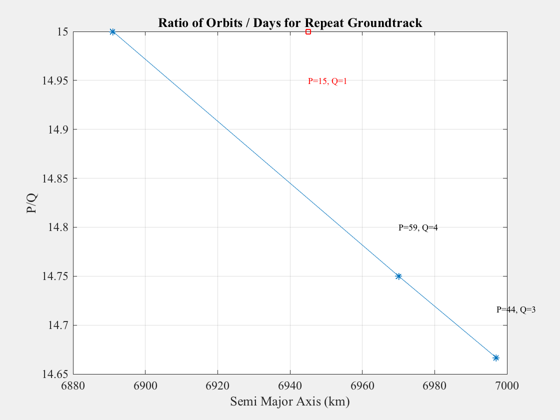
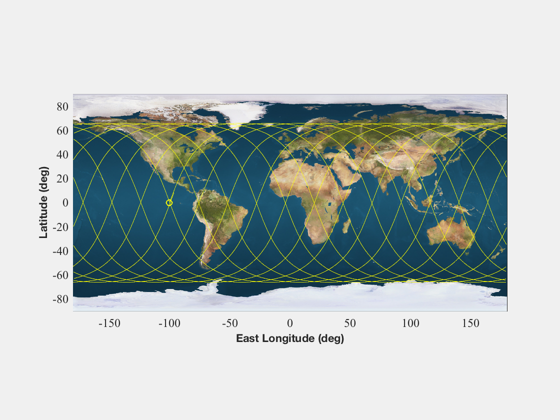
%-------------------------------------------------------------------------- % Copyright (c) 2014 Princeton Satellite Systems, Inc. % All rights reserved. %-------------------------------------------------------------------------- % Desired characteristics of repeat track % 15 orbits per day at 66 degrees inclination %-------------------------------------------- g = struct; g.P0 = 15; g.Q0 = 1; g.inc = 66*(pi/180); g.ecc = 0.01; g.da = 100; g.PMax = 15; g.QMax = 1; % Call the function and create a plot %------------------------------------ dGT = RepeatGroundTrack(g,1); % Get the Cartesian coordinates and simulate %------------------------------------------- [r,v] = El2RV([dGT.a(1) g.inc 0 0 g.ecc 0]); d = struct; d.j2 = 0.00108262563430956; d.a = 6378.137; d.mu = 398600.436; d.jD0 = 2455197.5; opts = odeset('RelTol',1e-12,'abstol',1e-12); tEnd = dGT.nodalPeriod(1); dOut = ode45( @(t,x) RHSGeoJ2(x,t,d), [0 tEnd], [r;v], opts ); % Plot the simulated track %------------------------- GroundTrack(dOut.y(1:3,:),dOut.x,d.jD0); %--------------------------------------