Magnetic levitation system simulation model. More...
#include <maglev.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| maglev (dsim_model_setup *setup) | |
| void | initialize_data () |
| void | initialization_complete () |
| Finish initialization. | |
| void | initialize_timestep () |
| Computation done prior to numerical integration. | |
| void | rhs (double t, double jd) |
| void | complete_timestep () |
| Computation done after numerical integration. | |
Protected Attributes | |
| dsim_variable | a_dsim |
| Scale dimension. | |
| dsim_variable | g_dsim |
| Acceleration of gravity. | |
| dsim_variable | l0_dsim |
| Inductance. | |
| dsim_variable | m_dsim |
| Mass. | |
| dsim_variable | i_dsim |
| Control current. | |
| dsim_variable | position_dsim |
| Position. | |
| dsim_variable | velocity_dsim |
| Velocity. | |
Magnetic levitation system simulation model.
Right hand side for a magnetic levitation system. The input is current.
The equation of motions are:
![\[\dot{x} = v\]](form_0.png)
![\[\dot{v} = f/m + g\]](form_1.png)
where f is the force due to the electromagnet. Since the force is proportional to current squared you must start the simulation with a positive offset from the equilibrium position. To compute iEq, the equilibrium current,
![\[ a = \sqrt{2}*\mu_0*l_M/\mu \]](form_2.png)
![\[ l_0 = \mu_0*n^2*2*a_M/a \]](form_3.png)
![\[ z = 1 + xEq/a \]](form_4.png)
![\[ iEq = \sqrt{2*a*m*g*z^2/l_0} \]](form_5.png)
where
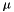 Relative permeability
Relative permeability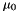 Permeability of free space
Permeability of free space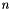 Wire turns
Wire turns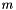 Mass
Mass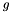 Acceleration of gravity
Acceleration of gravity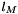 Magnet length
Magnet length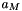 Magnet area
Magnet areaReferences: Woodson, H. H., J. R. Melcher, "Electromechanical Dynamics", John Wiley & Sons, 1968, pp. 192-200.
Definition at line 52 of file maglev.h.
| void maglev::initialize_data | ( | ) |
Initialize model data. Create the inputs, parameters, and states. The states are position and velocity.
Definition at line 28 of file maglev.cc.
{
// Parameters
const double pi = 3.14159265358979;
double lMagnet = 0.01; // Magnet length
double aMagnet = pi*pow(0.005,2); // Magnet area
double mu = 5000e-6; // Transformer steel
double mu0 = 4e-7*pi; // Permeability of free space
double n = 100; // Wire turns
double a = sqrt(2.0)*mu0*lMagnet/mu; // Scale factor
double l0 = mu0*pow(n,2)*2*aMagnet/a; // Inductance
double m = 0.01; // Mass
double g = 9.806; // Acceleration of gravity
double i = 0; // Current
double position = 0;
double velocity = 0;
i_dsim = create_input("i", sd_type_double, &i, 1,1, "A", "Current"); i_dsim.mark_telemetry();
a_dsim = create_parameter("a", sd_type_double, &a, 1,1, "Nm/A^2", "Scale"); a_dsim.mark_telemetry();
g_dsim = create_parameter("g", sd_type_double, &g, 1,1, "m/s^2", "Acceleration of gravity"); g_dsim.mark_telemetry();
l0_dsim = create_parameter("l0", sd_type_double, &l0, 1,1, "H", "Inductance"); l0_dsim.mark_telemetry();
m_dsim = create_parameter("m", sd_type_double, &m, 1,1, "kg", "Mass"); m_dsim.mark_telemetry();
position_dsim = create_integrated_state("position", sd_type_double, &position, 1,1, "m", "Position"); position_dsim.mark_telemetry();
velocity_dsim = create_integrated_state("velocity", sd_type_double, &velocity, 1,1, "m/s", "Velocity"); velocity_dsim.mark_telemetry();
configure_timestep(false,true,false);
}
| void maglev::rhs | ( | double | t, |
| double | jd | ||
| ) |
Computation done during numerical integration. Compute the derivatives for position and velocity.
Definition at line 75 of file maglev.cc.
{
double a = a_dsim.value_as_double();
double l0 = l0_dsim.value_as_double();
double m = m_dsim.value_as_double();
double g = g_dsim.value_as_double();
double i = i_dsim.value_as_double();
double position = position_dsim.value_as_double();
double velocity = velocity_dsim.value_as_double();
double f = -(0.5/a)*l0*pow(i,2)/pow(1 + position/a,2);
double accel = f/m + g;
position_dsim.set_derivative(velocity);
velocity_dsim.set_derivative(accel);
}
 1.7.2
1.7.2